Printable Medication Administration Record Sheet Form in PDF
The Medication Administration Record Sheet is a vital document used in healthcare settings to track the administration of medications to patients. This form helps ensure that each medication is given at the correct time and in the appropriate dosage, promoting patient safety and effective treatment. By accurately recording medication details, healthcare providers can maintain clear communication and accountability in patient care.
Open Medication Administration Record Sheet Editor Here
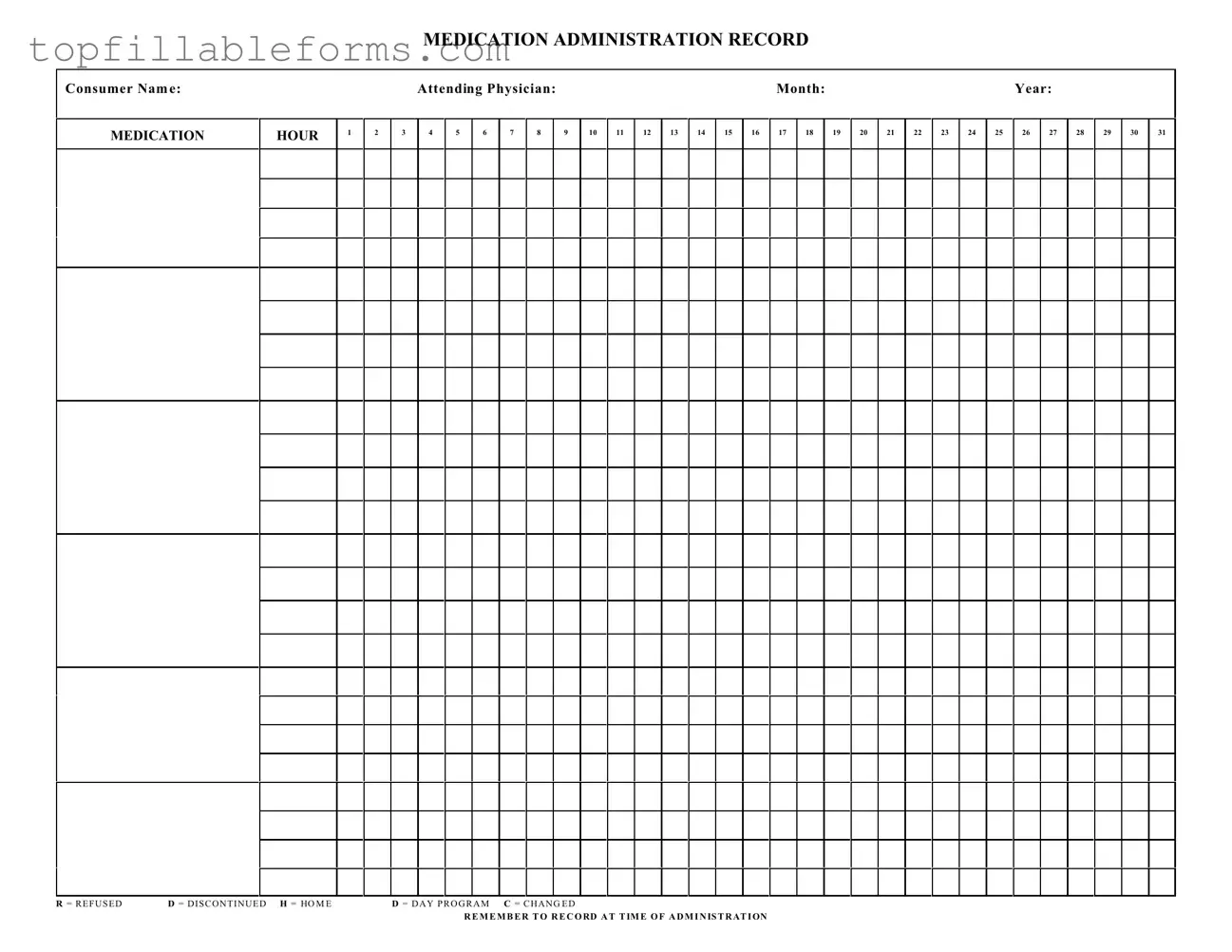
Printable Medication Administration Record Sheet Form in PDF
Open Medication Administration Record Sheet Editor Here
Finish the form now and be done
Finish your Medication Administration Record Sheet online by editing, saving, and downloading fast.
Open Medication Administration Record Sheet Editor Here
or
▼ PDF File